No-Code Integration Platforms
A no-code solution enables applications to communicate seamlessly with each other.

No code solutions
Every application or website these days communicates with the outer world with an API. Let it be an online shop using a reservation system and a connected database, or crucially a payment system like Mastercard to facilitate procurements.
Setting up such connections might prove challenging. Therefore platforms offer solutions, where it is basically possible to drag and drop applications, which should be connected. To connect such a service, an API is in a majority of cases used.
One company offering such solutions is Make. Alternatives might be Zapier, IFTTT, or Microsoft Power Automate.
API
The APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are gaining lately a rise in popularity, especially in connection with AI APIs. A lot of companies are trying to keep up with the latest trends and implement an AI API in some way.
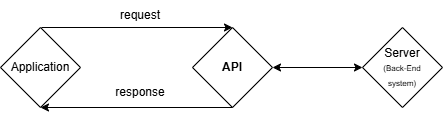
Application Programming Interface (API) is "a set of functions and procedures allowing applications to be created to access features or data of operating systems, applications, or other services.", CloudNowTech.
The key concepts are:
- Requests & responses – our application sends a request to an API
- Endpoints – specific URLs, where API services are available
- Authentication – some APIs require authentication using API keys, OAuth, or tokens
- Formats – APIs return mostly data in JSON or XML
WebHook
Webhooks serve a similar purpose as APIs. Whereas an API send and requests data, the webhook's data is sent automatically allowing real-time communication. It is pointed out that webhooks tend to be referred to as reversed APis, since they push data instead of pulling them.
OAuth
OAuth (Open Authorization) is an open standard for access delegation commonly used to allow users to grant websites or applications limited access to their data without exposing their credentials (e.g., passwords). It is widely used for authentication and authorization in web and mobile applications.
The newer version OAuth 2.0 shows wide adoption, offering more flexibility, and using access tokens, in comparison to OAuth 1.0 with a more complex structure and using cryptographic signatures. An access token is a string of characters, short lived (expires after a set period). Similarly as used in GitLab. Generally, ways of authorization are SSO, Federated Access, Delegated Authentication, Kerberos, Cross-Domain Trust.
Try your setting up an own application at Make.com, and see provided links [1, 2, 3, 4]. Make DevTool extension additionally supports the app development.
JSON
(JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format that is easy to read and write for both humans and machines. It is widely used for transmitting data between a server and a web application, as well as in APIs and configurations. JSON's syntax is straightforward, making it easy to understand and work with. Compared to XML, JSON uses fewer characters and is less verbose, making data transmission faster.
Make.com uses JSONC as a superset of JSON.
With enabled line comments // and block comments /* */.

Other supersets [1, 2] are XML, YAML, CSON,...
REST
Make.com makes use of REST and in some cases GraphQL. REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for designing networked applications. It is based on a set of principles that define how web standards like HTTP should be used to create scalable and maintainable web services. RESTful APIs use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) for operations. Resources can be represented in various formats like JSON, XML, or HTML.
Other protocols are depicted in the animation.
Source: LinkedIn
Future directions
It might be interesting to see in the future, how agents might be implemented in the workflow to connect the apps.